Amblyopia – Complete loss of vision in one eye because of an undetected meningioma
22/06/2020 07:34
Doctors said that without timely treatment, patient might have various complications such as loss of vision of the remaining eye or even death.
A female patient, Ms. P. T. L. (64 years old, from Lang Giang district, Bac Giang Province), was transferred to Viet Duc University Hospital due to completed loss of vision of the right eye and declining vision of the left side.
Based on analysis of clinical signs, CT scanner and MRI images, a diagnosis of a meningioma located at suprasellar site was confirmed. This tumor compressed and pushed the pituitary gland with optic chiasm downward, covered around right middle cerebral artery and 2/3 diameter of bilateral carotid arteries. It covered also the whole right optic nerve while contacted with the left one.
Dr. NGUYEN Duc Anh – Neurosurgery II Department, Viet Duc University Hospital shared that Ms. P. T. L. had a late-detected a meningioma at suprasellar area (after about 10 years) made the invasion to cerebral vessels and compromised vision.
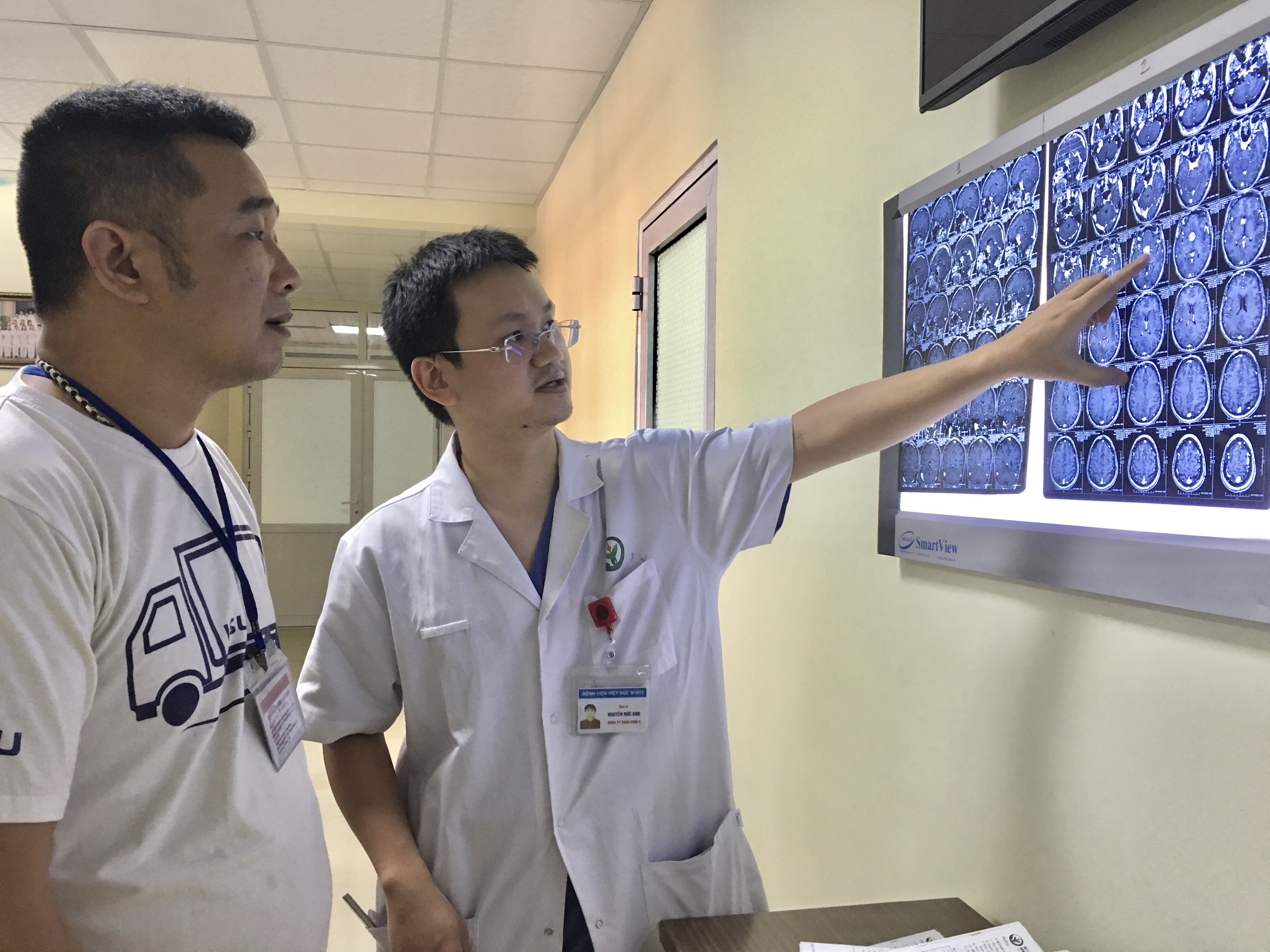

Doctor was explaining on X ray results to patient’s family
Without timely treatment, patient might have various complications such as loss of vision of the remaining eye or eventually death.
So doctors tried to convince patient’s family to accept the surgery as soon as possible, advised them to be cared by uncertified tradition medicine it might cause no chance for any further treatments.
After being accepted by patient’s family and the patient’s condition is suitable for anesthesia inquired, a 6-hour operation was performed.
“For such kind of operation, it’s required the specialized and qualified surgeon because a single negligence might lead to damages many things such as optic nerve, pituitary gland and cerebral arteries. After the operation, patient still face the complication as pituitary deficit, loss of vision, hemiplegic and the most serious complication, death” emphasized Dr. Nguyen Duc Anh.
After the surgery, patient was totally awake because the tumor was completely removed, all structures of optic nerve (cranial nerve II), pituitary gland stem, cerebral arteries were reserved.
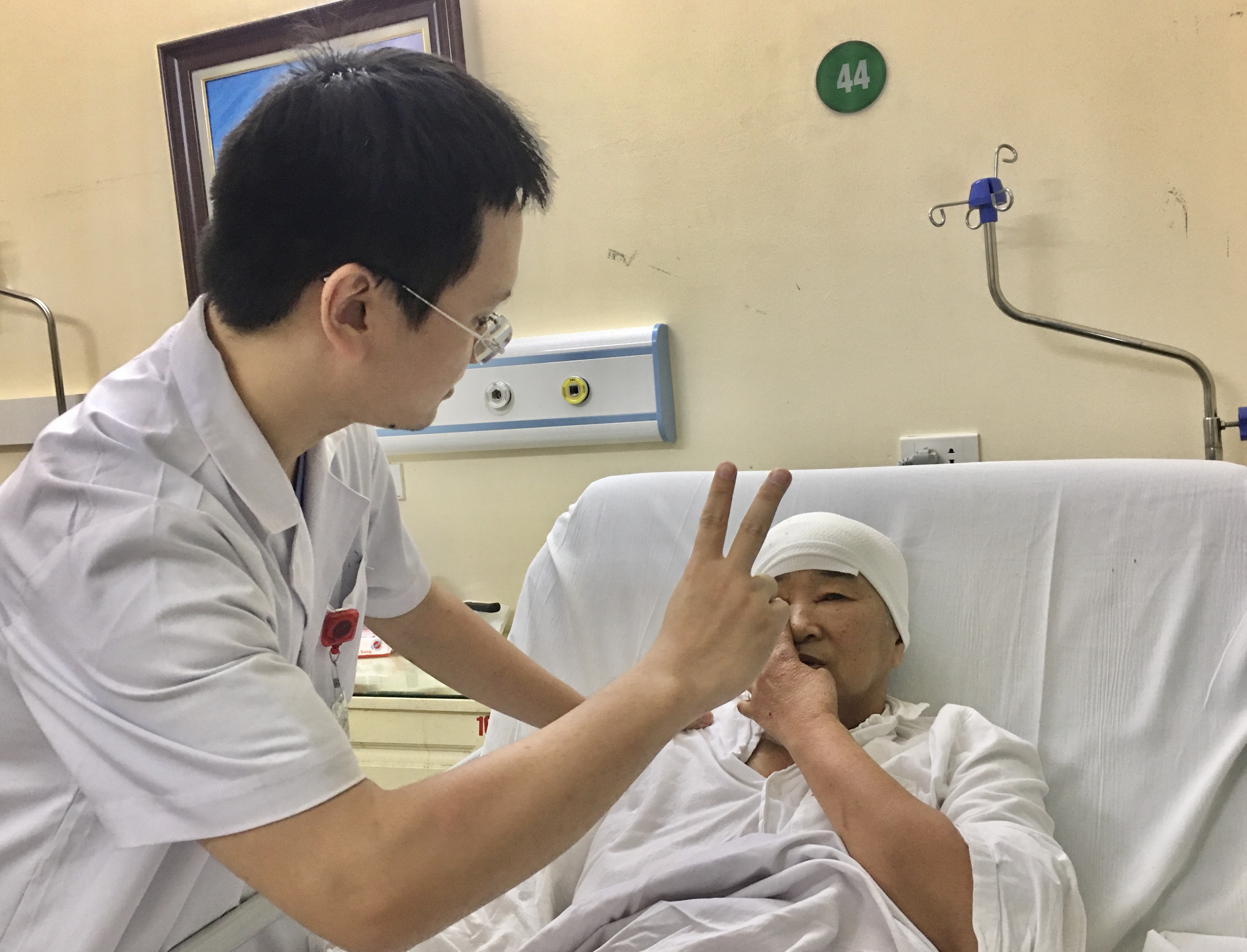
Postoperative vision check-up
From this case, doctors recommended that symptoms of brain tumor might be confused with other pathologies so many subjective people do not seek timely diagnosis and treatment.
Therefore when there are any sign such as insomnia, blurry vision, partial or complete loss of vision, diplopia, strabismus (crossed eyes), tinnitus, hearing loss, deafness, facial numbness, increasing weakness or paralysis, convulsion or other signs such as behavior and character changes, memory decline, sleeping disorders…, patients are required to go to a qualified medical facilities for early detection and timely intervention.
Late-detected meningioma might lead to complications such as vision loss, hemiplegic, speaking or hearing loss, coma and death.