Saving a multi-traumas patient with embolism due to thrombosis
22/01/2021 07:24
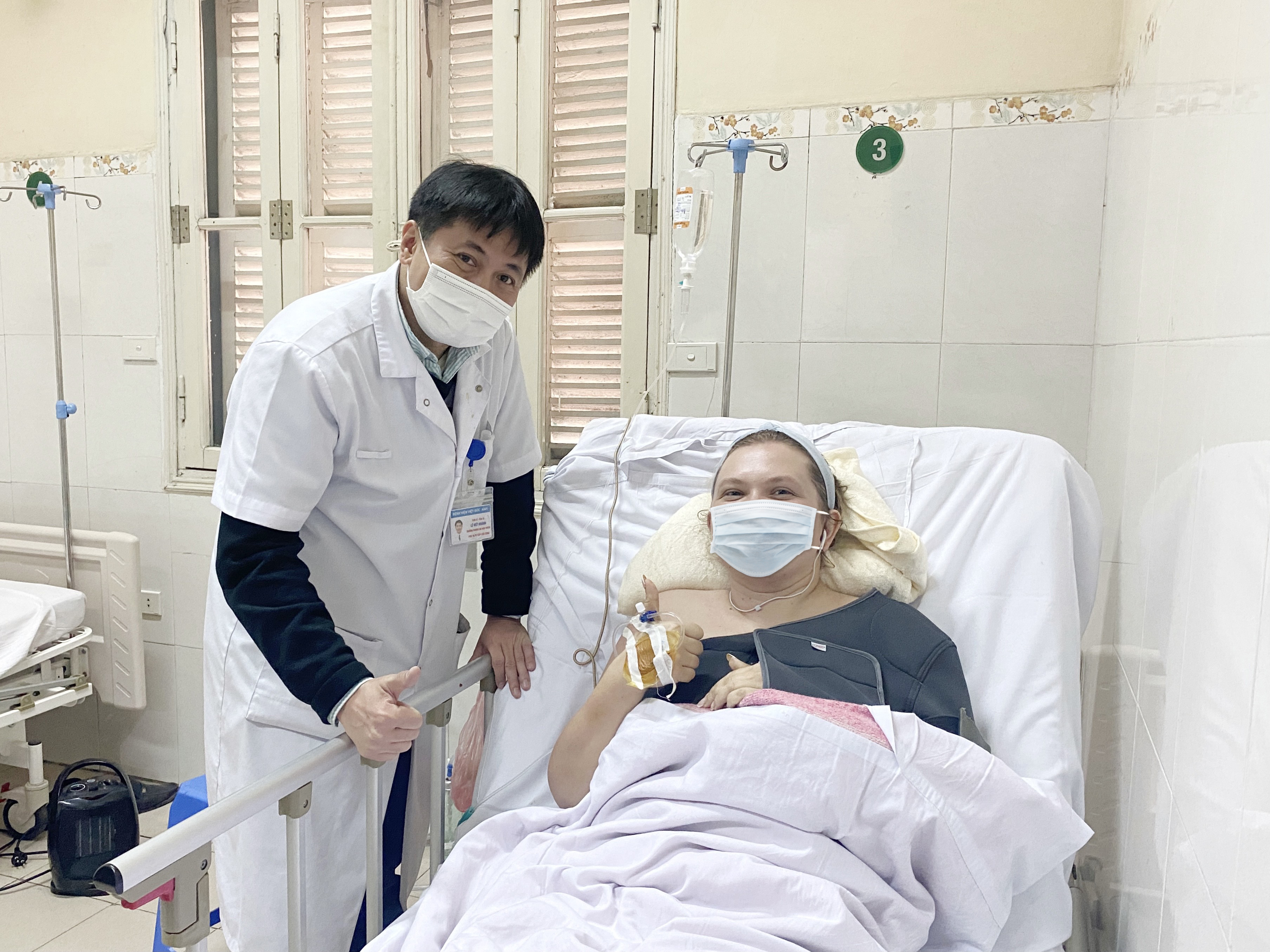
Mr. Le Viet Khanh, MA, Deputy head of Emergency Abdominal Surgery Department, Viet Duc University Hospital congratulates patient on recovering.
Thromboembolism in patients with multiple trauma is one of the causes of death. Recently, Viet Duc University Hospital has promptly saved a 35-year-old female patient (Ukrainian national) who was living and working in Hanoi, hospitalized in this critical situation.
On December 14th, 2020, Viet Duc University Hospital received a patient who got traffic accident, was admitted to hospital, alert and good communication, chest pain caused limited breathing. In here, patient was examined and diagnosed with multiple injuries: closed chest injury caused by multiple rib fractures with eight left ribs and two right ribs, broken bones penetrating into lung causing damage, associated with sternum fracture, left scapula fracture with lung damage causing atelectasis, pneumohemothorax.
Besides, patient has liver injury category IV and spleen injury category II are indicated for conservative treatment. At the beginning of being injured, patient has a very high risk of bleeding due to multiple injuries, the risk of liver bleeding is two and may need emergency surgery, so it is not allowed to use anticoagulant to prevent thrombosis.
Dr. Le Viet Khanh, PhD, Deputy head of Emergency Abdominal Surgery Department, Viet Duc University Hospital said: patient was drained by chest tube both sides, indicated for conservative treatment without surgery of liver and spleen.
During treatment from 14 to 28-12-2020, patient was in pain and limited movement, because of the risk of bleeding due to liver and spleen trauma, there is no anticoagulant prophylaxis. After six days, patient’s hemodynamic condition gradually stabilized.
However, on December 29th, patient showed signs of chest pain, coughing, difficulty breathing. On CT scan, the peripheral pulmonary artery thrombosis was detected on the left upper lobe parietal branch of lung, the other of the right pulmonary artery and left lung have no thrombosis; right pleural effusion is 9mm thick, left pleural effusion is 23mm thick; partial collapse of parenchyma of right and left upper and lower lobes close to bilateral effusion area; lower extremity blood vessel ultrasound did not detect deep vein thrombosis.
Doctors at Viet Duc University Hospital diagnosed pulmonary artery thrombosis in the left upper lobe of lung, the patient was treated with low – molecular – weight heparin. Patient has no clinical signs of hemorrhage and embolism. She is stable and has no more breathing problems and was maintained as above heparin dose during hospital stay and switched to oral anticoagulants upon discharge.
Dr. Le Viet Khanh, PhD added: Thromboembolism in patients with multiple trauma is one of the causes of death when the patient limits movement, damages blood vessels and increases the release of blood clotting activators from where the blood is hit.The two most common types of thrombosis in trauma patients are deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Every year, in Vietnam, more than 10 thousand people die from traffic accidents, and tens of thousands injured people are hospitalized. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism cause of late death after a few days or weeks in trauma or postoperative patients.
The risk’s factors include multiple trauma, spinal trauma with hemiplegia, blood vessels damage, and limited movement. Besides, some other factors such as obesity, smoking, use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement, lack of factor V Leiden congenital would also increase the risk of blood clots.
In particular, patients show signs of hypercoagulation when doing elastic blood clot test, doubling the rate of deep vein thrombosis compared to patients with no signs of hypercoagulation. Preventive measures for thrombosis are frequently used with appropriate anticoagulant doses, pressure elastic bandages, and early movement. The patient will be diagnosed early based on tomography, an ultrasound of blood vessels in patients with high D-Dimer and thrombotic treatment with anticoagulants, vascular intervention or surgery to take blood clots or fibrinolysis depending on each specific case.