Understanding of congenital scoliosis
12/08/2020 07:19
1.Congenital scoliosis definition.
Congenital scoliosis is a deflection of the spine that originates from birth. The rate of babies born with a congenital scoliosis is 1 in 10,000.
Associate Professor Dinh Ngoc Son, MD, Head of Spine Surgery Department, Viet Duc Unversity Hospital said: Congenital scoliosis occurs when the vertebrae is incomplete during fetal development. This type of scoliosis can have a wide range of symptoms, from mild symptoms to severe, life-threatening symptoms. Because the spine develops at the same time as the other organs of the body during the first weeks of the fetus, many children are born with scoliosis associated with other defects from bladder, kidneys, nervous system, cardiovascular system.
2. Symptoms of Congenital scoliosis.
Although congenital scoliosis has a fetal cause, symptoms may not be clear immediately after birth. Usually the child’s symptoms will be more visible during his/ her development. Common symptoms include:
– Shoulders are not balanced.
– Hips are not balanced.
– Head is not aligned with the body.
– When the child bends forward, the back will be low and low, the two sides are not equal.
Children with congenital scoliosis may have other symptoms, such as:
– Unusual patches of hair or pigmentation.
– Bulging mass in the ribs or back.
– Fatigue, twitching muscles from lower body.
– Deformity in hands and feet.
– Hearing loss
– Bladder sphincter disorders (urinary retention or incontinence).
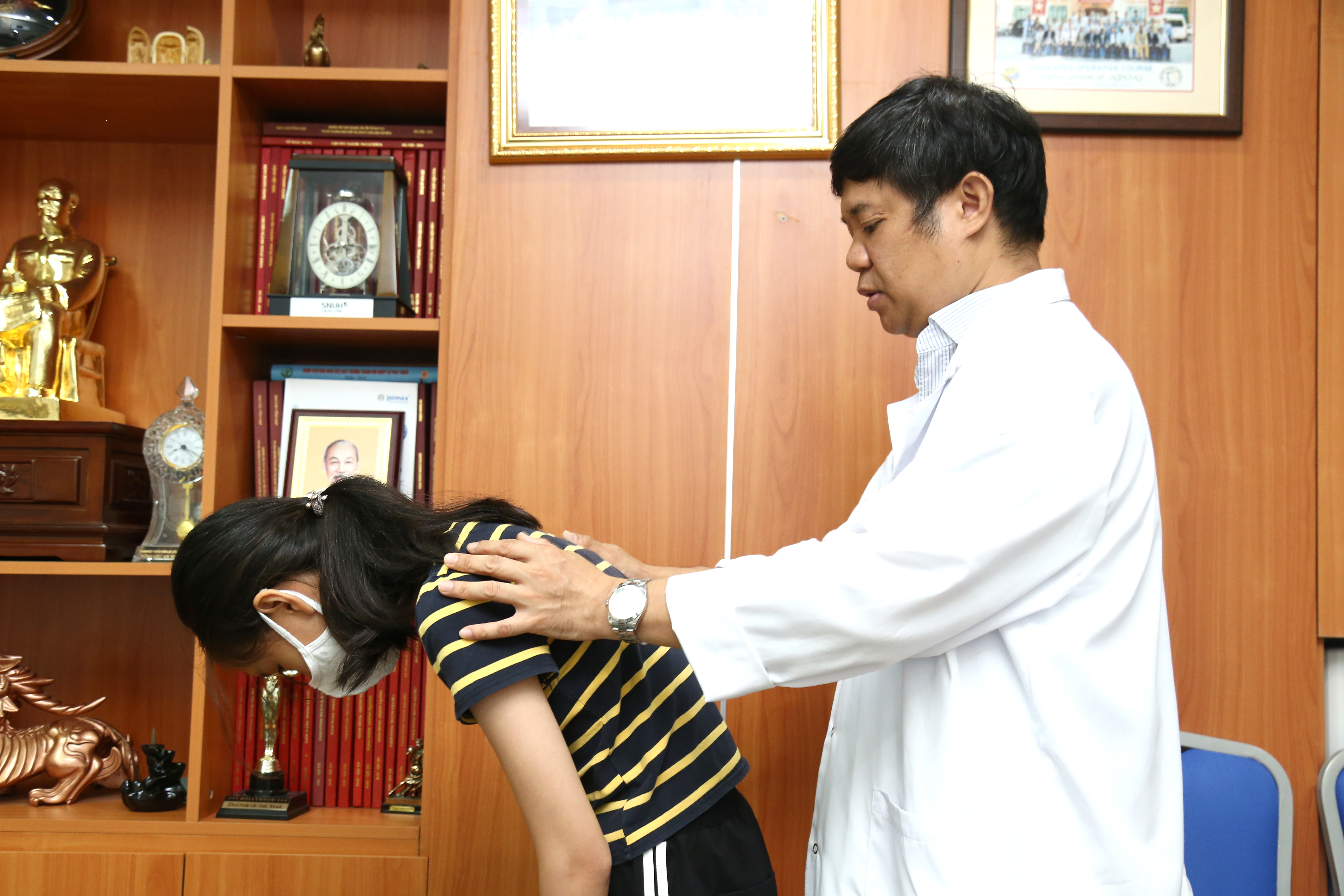
Associate Professor Dinh Ngoc Son, MD – Head of the Department of Spine Surgery examines the patient.
3.Cause of Congenital scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis occurs in infancy during which one or several vertebrae do not form completely. The result is a vertebral half-defect that leads to a wedge-shaped vertebra, or fuses on one side of the vertebrae.
4. Congenital scoliosis diagnosis
To diagnose congenital scoliosis, the doctor will have to make a physical examination of the child, fully exploit his/her history. After that, The child will have an X-ray of the entire spine. Approximately 30-40% of children have other associated defects to which means they may need additional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine, abdominal ultrasound, urinary system ultrasound, echocardiography, lung function measurement.
5.Treatment of congenital scoliosis
Treatment of congenital scoliosis depends on the age and severity of the scoliosis curve. Some children have slight curvature and mild symptoms that can be treated with routine follow-up. If the curvature is greatly increased, the child will likely need surgical treatment. Splints also have no impact on congenital scoliosis.
6.Surgical treatment
– Depending on the age, the degree of curvature and the speed of the progression of the scoliosis, doctors will prescribe suitable according to the child’s disease.
– Growth brace: Applies to young children (usually under 10). The doctor will place screws and braces that can stretch according to the child’s development. Every 6-12 months, he/she will have a splint stretch depending on the doctor’s follow-up visit.
– Cut half deformed body, correcting with screw brace.
In order to advise people how to detect and treat scoliosis early, Viet Duc University Hospital will organize an EXAMINATION AND FREE CONSULTING PROGRAM OF SCOLIOSIS with some helps from many leading spinal specialists
Especially, when people participate in the program, they will receive free X-rays of the entire spine.
Time : August 22, 2020 (Saturday).
Location: Clinic No. 10, Floor 2, Building C4, Medical Examination at on-demand area of Viet Duc University Hospital.
To get free consultation and consultation, people can register directly through telephone exchange 19001902.